With the latest release of BI Publisher 11.1.1.6 we eliminated many steps out of your way to enable the BI Publisher Auditing and Monitoring.
Here is a list of the steps.
- Enable Auditing from BI Publisher Administrator UI
- Run RCU to create IAU schema
- Create JDBC connection pool with WebLogic Console
- Set Audit Level with EM Console
- Register JDBC connection for Audit Policy Store with EM Console
You still need to go through the above 5 steps, but hey, compared to the previous release where you had to manually modify some configuration files, run sql script, copy files, etc, now it got much more simple and easier!
Let's take a look at the each step.
1. Enable Auditing from BI Publisher Administrator UI
Only thing you need to do for this step is to check 'Enable Monitor and Audit'. It’s that simple.
1. Go to Administrator page and click 'Server Configuration' menu
2. Scroll down to the bottom, and check 'Enable Monitor and Audit', then hit 'Apply' button.
2. Run RCU to create IAU schema
You need to run RCU to create IAU schema as you would have needed to do with older releases. But the cool thing is that now this process also runs a script to create a table (xmlpserver) to store all the BI Publisher specific information, so no need to run a separate sql script!
1. Go to RCU folder/directory to run RCU.
This step is basically exactly the same as before.
Here are the steps:
- Go to $RCU_HOME/bin and execute the ‘rcu’ command
- Choose Create at the starting screen and click Next.
- Enter your database details and click Next.
- Choose the option to create a new prefix, for example ‘BIP’, ‘KAN’, etc.
- Select 'Audit Services' from the list of schemas.
- Click Next and accept the tablespace creation.
- Click Finish to start the process.
3. Create JDBC Connection with WebLogic Console
Now, you need to create a JDBC connection on your WebLogic Server for the RCU scheme you just created so that the Audit Framework can access to the schema and start loading the auditing log data.
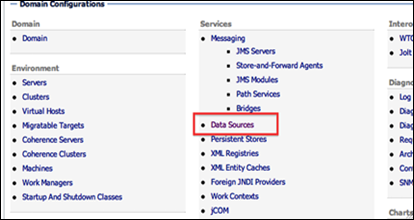
- Connect to the Oracle WebLogic Server administration console:
http://hostname:port/console (e.g. http://report.oracle.com:7001/console) - Under Services, click the Data Sources link.
- Click ‘Lock & Edit’ so that you can make changes (If not done yet)
- Click New –> ‘Generic Datasource’ to create a new data source.
- Enter the following details for the new data source:
Name: Enter a name such as ‘bip_audit_datasource.
JNDI Name: jdbc/AuditDB
Database Type: Oracle - Click Next and select ‘Oracle's Driver (Thin XA) Versions: 9.0.1 or later’ as Database Driver (if you’re using Oracle database), and click Next.
- The Connection Properties page appears. Enter the following information:
Database Name: Enter the name of the database (SID) to which you will connect.
Host Name: Enter the hostname of the database.
Port: Enter the database port.
Database User Name: This is the name of the audit schema that you created in
RCU. The suffix is always IAU for the audit schema. For example, if you gave
the prefix as ‘KAN’, then the schema name would be ‘KAN_IAU’.
Password: This is the password for the audit schema that you created in RCU. - Click Next.
- Accept the defaults, and click Test Configuration to verify the connection.
- Click Next
- Check listed servers where you want to make this JDBC connection available.
- Click ‘Finish’
Make sure you click ‘Activate Changes’ at the left hand side top to take the new JDBC connection in effect.
4. Set Audit Level with EM Console
Now you can set a level of the auditing for each BI Publisher’s auditing type by using Fusion Middleware Control (a.k.a. Enterprise Manager).
1. Login to Fusion Middleware Control UI
http://hostname:port/em (e.g. reporting.oracle.com:7001/em)
2. Access to Audit Policy configuration UI from the menu
Under WebLogic Domain, right-click bifoundation_domain, select Security and then click Audit Policy.
3. Set Audit Level for BI Publisher.
While you can select ‘Custom’ to set a customized level of Auditing for each component, you can simply select ‘Medium’ to enable all the BI Publisher related auditing.
5. Register JDBC connection for Audit Policy Store with EM Console
Finally, you can register the JNDI/JDBC data source to store your Auditing data. In order to do that, you just need to register the JDBC connection you created in the previous step as ‘Audit Store’ with Fusion Middleware Control (EM). Here are the steps:
1. Login to Fusion Middleware Control
2. Navigate to Weblogic Domain, right click on ‘bifoundation…..’, select Security, then Audit Store.
3. Click the searchlight icon next to the Data Source JNDI Name field.
4.Select the Audit JNDI/JDBC data source you created in the previous step in the pop-up window and click OK.
5. Click Apply to continue.
Now, you need to restart the WebLogic Server to take all the changes in effect.
Completing these steps, you should be able to start seeing all the BI Publisher related auditing data in the database scheme. As I have demonstrated in the previous post, now you can use BI Publisher to start visualizing the data.
If you are not seeing any data in IAU_BASE or XMLPSERVER table, then you might want to check the log file, which is located at $BI_HOME/user_projects/domains/bifoundation_domain/servers/AdminServer/logs/AdminServer-diagnostic.log
And lastly, here is a video that shows you the power of BI Publisher Auditing and Monitoring.
Happy Auditing and Monitoring!